L’argomento è oggetto di moltissimi studi e ricerche sia scientifiche che report giornalistici.
L’articolo di seguito, integralmente riportato, è una presentazione completa delle problematiche correlate al consumo di prodotti contenenti glutine.
In evidenza
“il riconoscimento delle diverse forme cliniche dovute all’ingestione di glutine”.
“l’importanza di un esame d’insieme della problematiche afferenti questa patologia come l’infiammazione della mucosa intestinale, l’equilibrio della flora intestinale, la giusta presenza degli enzimi digestivi, la correzione del deficit di assorbimento e l’aspetto immunologico”.
“la parte riguardante i danni che il glutine può arrecare alla mucosa intestinale e in che modo li provoca”.
DISTURBI CORRELATI AL CONSUMO DEL GLUTINE
Filip Dudal D.O. Institute for Functional Medicine Certified Practitioner (IFMCP) USA
“Generalmente si considera che il Morbo Celiaco sia l’unica forma di disturbo causato dall’ingestione del glutine. In realtà diversi studi scientifici, condotti dal Dr. Alessio Fasano della Harvard University, dimostrano che esistono una serie di disturbi correlati al consumo del glutine che vanno ben oltre la conclamata celiachia. Le proteine del glutine non vengono sempre completamente digerite. Ciò produce una grande quantità di sostanze che provocano una risposta immunitaria e infiammatoria cronica soprattutto nei soggetti geneticamente predisposti e in forme minori si può presentare in soggetti che non lo sono.
Sfatiamo il luogo comune. Tanti pensano che l’ingestione del glutine porti unicamente a problemi digestivi. Non è così. Il glutine può essere causa di altri sintomi definiti extra digestivi quali: dolori articolari, herpes, dermatiti, astenia, asma, disturbi neurologici e cognitivi (difficoltà di concentrazione, di memoria, lentezza mentale e abbassamento del tono
dell’umore). La mancanza di sintomi digestivi fa sì che quelli extra-digestivi sopra citati non vengano riconosciuti come correlati al consumo del glutine. In realtà, come vedremo nel corso di questo articolo, l’assunzione di glutine provoca diverse forme cliniche.
L’esposizione cronica al glutine in persone sensibili causa un’alterazione della barriera intestinale e della sua funzione selettiva di assorbimento. Ne risulta un malassorbimento delle sostanze nutritive necessarie al buon funzionamento del metabolismo corporeo.
Vi sono diversi gradi di reazione immunologica al glutine che si traducono in diverse forme cliniche.
Non si tratta sempre e solo di “celiachia o non celiachia ”. Il quadro è più complesso e comprende alcune forme allergiche, forme auto-immuni e forme non-allergiche. Si rendono dunque necessari dei test che possano mettere in evidenza ogni grado di reazione al glutine.
Il trattamento delle varie forme cliniche non deve essere solo limitato all’esclusione del glutine dall’alimentazione. Vanno considerate l’infiammazione della mucosa intestinale, l’equilibrio della flora intestinale, la giusta presenza degli enzimi digestivi, la correzione del deficit di assorbimento e l’aspetto immunologico. Una volta riconosciuta e confermata la forma clinica specifica con un pannello completo di esami di laboratorio su sangue, sulle feci e sulla mucosa orale si avranno tutti gli elementi necessari per instaurare un trattamento personalizzato ed efficace.
Per saperne di più
Il glutine è la principale proteina strutturale che compone il frumento ed è contenuto anche in altri cereali come il farro, la segale, la spelta e l’orzo.
Tante persone pensano che il Kamut® contenga meno glutine. In realtà è l’esatto contrario.
Il grano Khorasan a marchio Kamut® di origine egiziana contiene glutine spesso in quantità maggiore del frumento stesso. Fu introdotto negli Stati Uniti nel 1949 e fu dapprima denominato “Grano del Re Tut” per poi essere registrato come marchio Kamut® nel 1990.
Nell’era moderna l’industria alimentare ha favorito la selezione, lo sviluppo e la coltivazione delle varietà di grano che hanno la più alta concentrazione di glutine. Sappiamo che il glutine ha un valore nutrizionale molto limitato, ma ha la caratteristica di rendere l’impasto della farina molto viscoelastico (maglia glutinica). Infatti, in una soluzione acquosa, alcune frazioni del glutine (gliadine e glutenina) interagiscono per formare una trama proteica che intrappola l’amido e i gas durante la fermentazione dell’impasto favorendo la creazione di un prodotto alimentare più performante alla vendita e alle leggi di mercato. Di fatto questo tipo di elaborato ha una maggiore lievitazione, una migliore resistenza alla cottura e una migliore palatabilità che permettono di creare prodotti più belli e attraenti. Se ci ricordiamo, la pasta di un tempo che conteneva meno glutine, era di taglio corto e di colore tendente al marrone. Sicuramente più invitante alla vista, sono i nuovi prodotti; dalla foggia attraente ma con più glutine e meno salutari. Caratteristiche queste che ovviamente consentono una più ampia commercializzazione.
La vasta scala necessaria all’industria alimentare per arrivare a profitti sempre maggiori ha penalizzato quei grani autoctoni con minore concentrazione di glutine e ha favorito l’importazione di grani transnazionali, come il grano tenero del Canada, che consente di produrre la farina Manitoba; una farina caratterizzata dall’elevato contenuto di gliadina e glutenina che rende più facile la cottura garantendo la ricercata pasta “al dente”.
In Europa, il consumo medio di glutine contenuto nelle farine è di 10-20 grammi al giorno. Alcuni segmenti della popolazione arrivano a 50 grammi al giorno per l’alto consumo di prodotti da forno e di pasta. Statisticamente il Nord Italia conta 1 celiaco su 130 individui, nel Sud Italia si conta 1 individuo celiaco su 100. Le forme di sensibilità al glutine non- celiaca sono ben più frequenti.
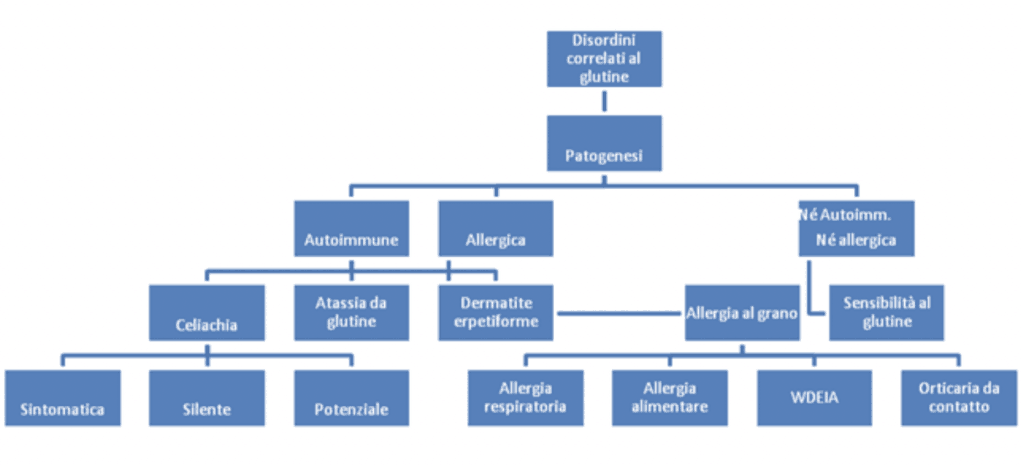
Quali sono le diverse forme cliniche dovute all’ ingestione del glutine?
A. Forme Autoimmuni
1. Celiachia (potenziale, silente o sintomatica)
2. Atassia da glutine (perdita del controllo e della coordinazione muscolare)
3. Dermatite erpetiforme (Herpes con depositi di IgA nelle pustole)
B. Forme Allergiche
1. Allergia al frumento
2. Allergia con manifestazioni respiratorie, asma
3. Anafilassi Asmatica Grano-Dipendente Indotta dall’Esercizio Fisico (WDEIA – Wheat Derived Exercice Induced
Asthma)
C. Forme Non-Allergiche
1. NCGS – Non-Celiac Gluten Sensitivity – Sensibilità al Glutine Non-Celiaca
2. Ipersensibilità al Glutine