Vedi anche: Approccio integrato alla riduzione dell’infiammazione cronica di basso grado
![]() In evidenza – Perché è un tema centrale
In evidenza – Perché è un tema centrale
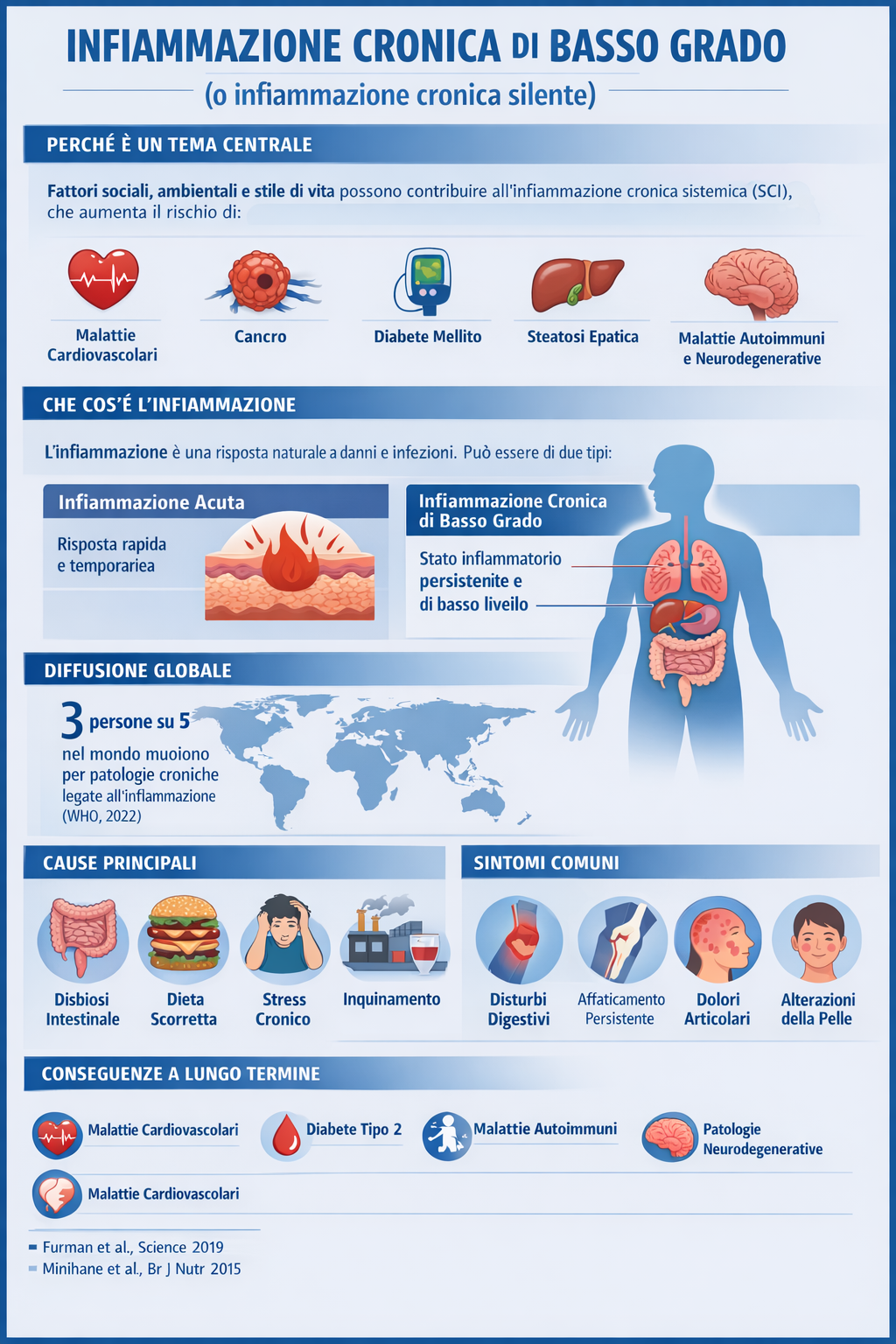
Sebbene l’aumento intermittente dell’infiammazione sia fondamentale per la sopravvivenza durante lesioni fisiche e infezioni, recenti ricerche hanno rivelato che alcuni fattori sociali, ambientali e legati allo stile di vita possono favorire l’infiammazione cronica sistemica (SCI) che, a sua volta, può portare a diverse patologie che, nel loro insieme, rappresentano le principali cause di disabilità e mortalità in tutto il mondo, come malattie cardiovascolari, cancro, diabete mellito, malattia renale cronica, steatosi epatica non alcolica e malattie autoimmuni e neurodegenerative.
Riferimenti
Furman et al., Science, 2019
Calder et al., Nutrients, 2017
Che cos’è l’infiammazione
L’infiammazione è una componente centrale dell’immunità innata (aspecifica). In termini generici, l’infiammazione è una risposta locale al danno cellulare caratterizzata da aumento del flusso sanguigno, dilatazione capillare, infiltrazione leucocitaria e produzione localizzata di una serie di mediatori chimici, che contribuiscono all’eliminazione degli agenti tossici e alla riparazione dei tessuti danneggiati. È ormai chiaro che la cessazione (in alternativa nota come risoluzione) dell’infiammazione è un processo attivo che coinvolge citochine e altri mediatori antinfiammatori, in particolare lipidi, piuttosto che una semplice interruzione delle vie pro-infiammatorie. L’infiammazione agisce sia come “amica che come nemica”: è una componente essenziale dell’immunosorveglianza e della difesa dell’ospite, tuttavia uno stato infiammatorio persistente nel tempo è una caratteristica patologica di un’ampia gamma di condizioni croniche.
Riferimenti
Medzhitov, Nature, 2008
Serhan et al., Nature, 2007
Infiammazione acuta
L’infiammazione acuta è la risposta rapida e a breve termine dell’organismo a lesioni o infezioni, caratterizzata da arrossamento, gonfiore, calore e dolore. È un processo benefico che aiuta a proteggere dai patogeni e ad avviare la riparazione dei tessuti. Sebbene possa durare da poche ore a qualche giorno, è diversa dall’infiammazione cronica, che persiste per periodi più lunghi e può essere dannosa. (nota personale: I classici segni di un’infiammazione acuta – calore, arrossamento, gonfiore, dolore – indicano che il corpo sta combattendo e guarendo).
Riferimenti
Abbas et al., Cellular and Molecular Immunology
Serhan et al., Nature, 2007
Infiammazione cronica di basso grado
L’infiammazione di basso grado, o “silente”, è una risposta immunitaria cronica, non infettiva e di bassa intensità che persiste per mesi o anni. È spesso innescata da obesità, stress metabolico e una cattiva alimentazione, che include non solo la scelta di cibi poco sani, ma anche processi digestivi incompleti e squilibri del microbiota.
Questa condizione è caratterizzata da marcatori ematici leggermente elevati, ma spesso tecnicamente entro i limiti di normalità (come la PCR), rendendo la diagnosi clinica estremamente complessa. Agisce come un “killer silenzioso”, fungendo da precursore per patologie gravi come il diabete, le malattie cardiache e il dolore cronico.
Gli aspetti chiave dell’infiammazione di basso grado includono:
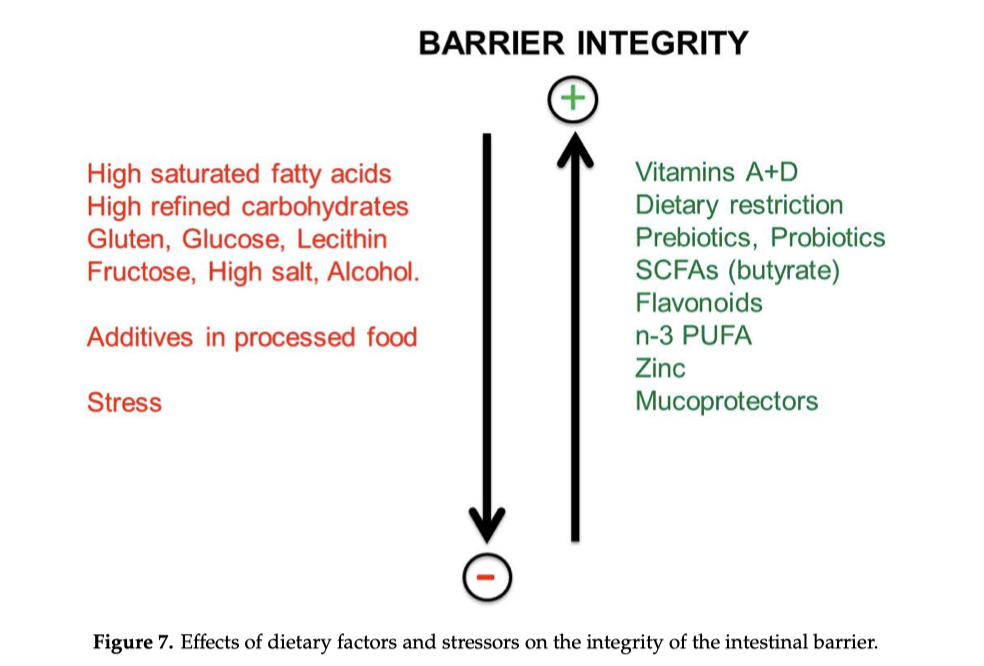
Cause multifattoriali: Oltre alla mancanza di attività fisica e ai fattori ambientali, giocano un ruolo cruciale i disturbi metabolici e le alterazioni della barriera intestinale. Quando il cibo non viene digerito correttamente, può innescare una reazione immunitaria persistente che alimenta lo stato infiammatorio.
Impatto sistemico: Questo stato cronico causa danni tissutali lievi ma continui, collegati direttamente a malattie come l’Alzheimer, il diabete di tipo 2, le patologie cardiovascolari e alcune forme di cancro.
Come diagnosticarla:
A. prima fase: Poiché gli esami standard non rilevano anomalie acute, la diagnosi deve basarsi sull’analisi di sintomi persistenti quali affaticamento ingiustificato, dolore cronico e alterazioni cognitive (nebbia cognitiva).
B. seconda fase: esame del sangue PCR ad alta sensibilità (hs-CRP). A differenza della PCR standard, la PCR ad alta sensibilità (hs-CRP) è in grado di misurare valori inferiori a 0.3 mg/dL, permettendo di vedere proprio quelle oscillazioni minime che altrimenti resterebbero invisibili.
C. terza fase: Interlukina IL-6. E’ un esame specialistico. Nella maggior parte dei laboratori, l’IL-6 è considerato “normale” fino a circa 5-10 pg/mL.
-
In un’infezione acuta, l’IL-6 schizza a 100 o 1000 pg/mL.
-
Nell’infiammazione di basso grado, l’IL-6 sale magari da 1 a 3 pg/mL.
Sebbene sia triplicata (e quindi indichi un problema), il risultato del laboratorio dirà comunque “Sotto il limite: NORMALE”. Ecco perché è un marcatore “sfuggente” per il medico di base, ma un “biomarcatore avanzato” per lo specialista che sa leggere le variazioni minime. Lo specialista spesso valuta l’IL-6 insieme al Rapporto Neutrofili/Linfociti (NLR), un calcolo semplice dall’emocromo che conferma se il sistema immunitario è in uno stato di allerta cronica.
Riferimenti
Minihane et al. British Journal of Nutrition (2015), 114, 999–1012 doi:10.1017/S0007114515002093 q ILSI Europe 2015”.
Review Article Low-grade inflammation, diet composition and health: current research evidence and its translation. Anne M. Minihane, Sophie Vinoyet et al.
Hotamisligil, Nature, 2006
Pearson et al., Circulation, 2003
Lucius, Integrative and Complementary Therapies, 2023
Infiammazione cronica di basso grado e infiammazione sistemica
Quando lo stato infiammatorio coinvolge simultaneamente più distretti dell’organismo si parla di infiammazione sistemica. Tale condizione può derivare sia dalla generalizzazione di un processo infiammatorio acuto, sia dalla progressiva estensione di uno stato infiammatorio cronico di basso grado inizialmente localizzato. L’intestino rappresenta uno dei principali siti di origine, grazie alla sua estesa superficie, all’intensa attività immunitaria e all’interazione con il microbiota. Tuttavia, il processo interessa numerosi organi e tessuti (vedi approfondimento A).
Riferimenti
Furman et al., Science, 2019
Franceschi et al., Cell, 2018
Diffusione globale
Le malattie croniche associate all’infiammazione rappresentano la principale causa di mortalità mondiale. Si stima che circa 3 persone su 5 nel mondo muoiano per patologie legate a processi infiammatori cronici.
“Chronic inflammatory diseases are the most significant cause of death in the world. The World Health Organization (WHO) ranks chronic diseases as the greatest threat to human health. The prevalence of diseases associated with chronic inflammation is anticipated to increase persistently for the next 30 years in the United States. in 2000, nearly 125 million Americans were living with chronic conditions and 61 million (21%) had more than one. In recent estimates by Rand Corporation, in 2014 nearly 60% of Americans had at least one chronic condition, 42% had more than one and 12% of adults had 5 or more chronic conditions. Worldwide, 3 of 5 people die due to chronic inflammatory diseases like stroke, chronic respiratory diseases, heart disorders, cancer, obesity, and diabetes. 2022”.
Riferimenti
Furman et al., Science, 2019
Cause e fattori scatenanti principali
-
Disbiosi intestinale: Alterazione della flora batterica intestinale, che può essere causata da dieta squilibrata, uso eccessivo di antibiotici o altre sostanze tossiche.
-
Dieta scorretta: Consumo eccessivo di cibi processati, ricchi di zuccheri raffinati e grassi saturi, che possono favorire l’infiammazione.
-
Stress: Lo stress cronico può influenzare negativamente il sistema immunitario e aumentare la suscettibilità all’infiammazione.
-
Inquinamento ambientale e tossine: Esposizione a sostanze chimiche presenti nell’ambiente o nei cibi può contribuire allo stress ossidativo e all’infiammazione.
Fumo e alcol: Questi fattori possono aggravare lo stress ossidativo e danneggiare le cellule, favorendo l’infiammazione.
Riferimenti
Cani et al., Diabetes, 2007
Tilg & Moschen, Gut, 2014
Egger & Dixon, AJPM, 2014
Slavich & Irwin, Psychological Bulletin, 2014
Sintomi comuni
-
Disturbi digestivi: Gonfiore, crampi addominali, diarrea o stipsi, che possono variare in intensità e frequenza.
-
Affaticamento persistente: Stanchezza cronica, mancanza di energia e difficoltà di concentrazione.
-
Dolori articolari: Dolori muscolari e articolari diffusi.
-
Alterazioni della pelle: Eruzioni cutanee, eczemi o altre manifestazioni cutanee.
-
Problemi del sonno: Difficoltà ad addormentarsi o a mantenere un sonno profondo.
-
Manifestazioni cutanee
Riferimenti
Dantzer et al., Brain Behav Immun, 2008
Miller et al., Biol Psychiatry, 2009
Conseguenze a lungo termine
Se non trattata, l’infiammazione intestinale di basso grado può contribuire allo sviluppo di malattie croniche come:
Malattie cardiovascolari: Aumento del rischio di infarto, ictus e altre patologie cardiovascolari. Diabete di tipo 2: Maggiore probabilità di sviluppare resistenza all’insulina e diabete.
Malattie autoimmuni: Maggiore suscettibilità a malattie come artrite reumatoide, lupus, ecc. Patologie neurodegenerative: Rischio aumentato di sviluppare malattie come Alzheimer o Parkinson.
Alcuni tipi di cancro: Aumento del rischio di sviluppare alcuni tipi di tumore.
Misure generali che possono aiutare a ridurre l’infiammazione includono:
Seguire una dieta equilibrata: Ricca di fibre, frutta, verdura e alimenti integrali, con un basso indice glicemico.
Ridurre il consumo di cibi processati, zuccheri raffinati e grassi saturi .
Gestire lo stress: Attraverso tecniche di rilassamento, meditazione, yoga o altre attività che aiutano a ridurre lo stress.
Mantenere un peso sano: L’obesità e il sovrappeso possono aumentare l’infiammazione.
Limitare il consumo di alcol e smettere di fumare .
Integrare con probiotici: Possono aiutare a ripristinare l’equilibrio della flora batterica intestinale.
Riferimenti
Estruch et al., NEJM, 2018
Calder et al., Br J Nutr, 2011
Nota:
L’infiammazione cronica di basso grado (o “silente”) è un fattore chiave nello sviluppo e nella progressione delle malattie cardiovascolari, inclusa l’aterosclerosi, l’ipertensione e l’infarto. Questo processo, spesso asintomatico, provoca una disfunzione endoteliale, stimola la formazione e la rottura di placche aterosclerotiche e può causare sindromi coronariche acute
Riferimenti
Ridker et al., NEJM, 2017
Libby, Nature, 2002
Casi paradigmatici
Obesità. L’obesità, soprattutto quella viscerale, è accompagnata da uno stato infiammatorio cronico di basso grado. Il tessuto adiposo in eccesso secerne citochine pro-infiammatorie (come TNF-α e IL-6) che contribuiscono allo sviluppo di insulino-resistenza. Non a caso nei pazienti obesi si riscontrano spesso livelli elevati di proteina C-reattiva (marker di infiammazione sistemica) e un maggior rischio di diabete di tipo 2. Intervenire sullo stile di vita per ridurre il peso (dieta equilibrata e esercizio) aiuta a “raffreddare” questa infiammazione metabolica, migliorando anche i parametri clinici.
La sindrome metabolica è strettamente legata a uno stato di infiammazione cronica di basso grado (o “silente”), in cui il grasso viscerale in eccesso agisce come organo endocrino, secernendo citochine pro-infiammatorie (come IL−6 e TNF−α ). Questo processo persistente, spesso definito “meta-infiammazione”, promuove l’insulino-resistenza, disfunzioni vascolari e il rischio di diabete e malattie cardiovascolari. Artrite reumatoide (malattia autoimmune)
Riferimenti
Wellen & Hotamisligil, J Clin Invest, 2003
Shoelson et al., J Clin Invest, 2006
Artrite reumatoide
L’artrite reumatoide (AR) è una malattia infiammatoria cronica autoimmune che colpisce principalmente le articolazioni, provocando dolore, gonfiore e rigidità simmetrica, spesso con esordio tra i 40-60 anni. Il sistema immunitario attacca erroneamente i tessuti sani, creando un’infiammazione cronica di basso grado che, se non trattata, porta a deformità e danni articolari progressivi Biomarcatori I marcatori per l’infiammazione di basso grado più comunemente utilizzati includono la proteina C-reattiva (PCR), l’interleuchina-6 (IL-6), il fibrinogeno, e le specie reattive dell’ossigeno (ROS). Questi marcatori possono essere misurati attraverso esami del sangue e indicano uno stato infiammatorio cronico che può essere associato a diverse condizioni di salute .
Riferimenti
McInnes & Schett, NEJM, 2011
Smolen et al., Lancet, 2016